Magnetic Order in Superconductors
The effects of magnetic impurities and the possibility of magnetic ordering in superconductors has had a rich and interesting history, and we have had a longstanding interest in investigating such systems. Magnetic impurities substituted into a superconductor were found to quickly suppress superconductivity due to the strong spin scattering that disrupts the Cooper pairs. Typically ~1% substitution was enough to completely extinguish the superconducting state, and such a low concentration of magnetic moments precludes the possibility of cooperative magnetic states forming and competing with the superconducting order parameter. The first exception to this behavior was realized for the (Ce1-x-Rx)Ru2 system, where over 30% of non-magnetic Ce4+ could be replaced by the magnetic heavy lanthanides before superconductivity was suppressed. Strong ferromagnetic correlations were found to develop in the superconducting state, but no long range order was present.
The first examples of true long range magnetic order coexisting with superconductivity were provided by the ternary Chevrel-phase superconductors (RMo6S8) and related (RRh4B4) compounds. In these materials there is a separate, fully occupied lanthanide sublattice. The fact that these materials were superconducting at all implied that the magnetic ions and the superconducting electrons belonged to different, "isolated", sublattices, and thereby the conventional Abrikosov-Gorkov spin-depairing mechanism was suppressed. The magnetic ordering temperatures are all low, ~1K, and thus it was argued that electromagnetic (dipolar) interactions should dominate the energetics of the magnetic system. For materials where these interactions favor antiferromagnetism the magnetization averages to zero on the length scale of a unit cell (a), which results in a weak influence on the superconducting state (a<<x,l). This is the most prevalent case found in nature, and apart from a few anomalies in properties such as the upper critical field, the antiferromagnetic order and superconductivity were found to readily accommodate one another. In the rare and more interesting situation where the magnetic interactions are ferromagnetic, there is strong coupling to the superconducting state that originates from the internally generated magnetic field. The competition with the superconducting order parameter gives rise to long wavelength oscillatory magnetic states and/or reentrant superconductivity. The studies of these materials contributed greatly to our understanding of these two competing phenomena, but the possible role of exchange interactions in these systems, and the related question of how the dipolar interaction alone could be responsible for the antiferromagnetism in some materials while others (with the same crystal structure) are ferromagnets, remained unexplained.
The cuprate superconductors offer new and interesting perspectives into our understanding of "magnetic superconductors" for a number of reasons. In the materials typified by RBa2Cu3O6+x (1-2-3) and R2Ba4Cu8O16 (2-4-8), for example, the R ions appear to be electronically isolated from the Cu-O layers where the Cooper pairs form, similar to the ternary superconductors, and the low lanthanide ordering temperatures (~1 K) suggested that the cuprate superconductors were again prototypical "magnetic superconductors". They were also interesting because the layered crystal structure, with c ~3a, rendered them naturally two-dimensional (2d) in nature, and indeed some of the best 2d magnets known belong to this class of materials. However, there are also examples where the magnetic ordering temperature is much too high to be explained by dipolar interactions, and it has become clear that R-R exchange interactions actually must play a dominant role in the magnetism, as is also clearly the case for the new RNi2B2C class of superconductors. In contrast to the ternary superconductors, in the cuprates there is no clear separation of the lanthanide sublattice from the superconducting electrons. Moreover, one of the most interesting aspects of the cuprates concerns the magnetism associated with the Cu ions, which is the same sublattice where the superconducting pairing occurs. The undoped cuprates are antiferromagnetic insulators where the S=1/2 Cu spins order at high temperatures, typically near or above room temperature. The in-plane Cu exchange interactions are much stronger than along the c-axis, and thus again the magnetism is two-dimensional in nature. With doping, the materials lose the Cu long range magnetic order and become high TC superconductors. However, the Cu moments and energetics are still present.
For the lanthanide magnetism, the overall behavior is quite different. In the single-layer R2CuO4 type materials the lanthanide exchange interactions are three dimensional in nature, and typically the Cu and R systems exhibit relatively strong coupling. For the multi-layered materials, on the other hand, the distance along the stacking axis becomes quite large, and this physical separation renders the ordering two-dimensional in nature, but for very different reasons than for the Cu system. The R-Cu interactions also tend to be weaker and the lanthanide sublattice appears to be relatively isolated from the rest of the system, making them prototypical 2d magnets with low ordering temperatures.
In all of these systems, for both the Cu magnetic order as well as the lanthanide magnetic order, the spin structures are relatively simple commensurate antiferromagnetic configurations. In particular, no materials have been discovered yet that exhibit a net ferromagnetic component, with its associated macroscopic magnetization. By commensurate we mean that the antiferromagnetic unit cell is a simple integer multiple of the chemical unit cell. Within the Cu-O planes, for example, the nearest-neighbor spins have always been found to be antiparallel, and the spins always point along a common direction (i.e., they are collinear) within the a-b plane. However, there can be the complication that some of the structures are noncollinear, by which we mean that the direction of the spins between the layers is not necessarily along the same crystallographic direction. The added complication of having both Cu and R moments can then make the magnetism of these cuprates quite rich and interesting.
In the following example we have rare earth ordering at low T, Ru magnetic ordering at quite high T, and coexistence of both types of long range antiferromagnetic order with superconductivity.


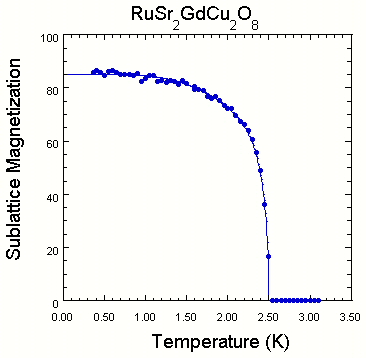
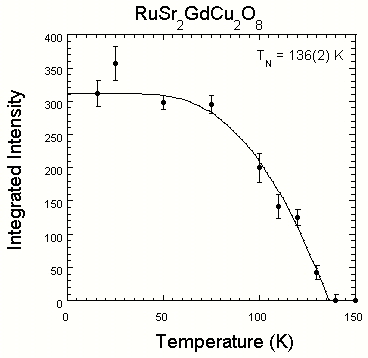
The figure on the left shows the development of long range antiferromagnetic order of the Gd moments in this superconducting material. This ordering occurs at low temperature and coexists with superconductivity, similar to many "magnetic superconductors" that have been investigated over the years (see list of publications below). The figure on the right side demonstrates that the Ru ions also carry a magnetic moment, and they order antiferromagnetically as well. This is the highest magnetic ordering temperature observed so far in a superconducting material. Phys. Rev. B 61, R14964 (2000).
We have also recently carried out an investigation of the magnetic properties of the superconducting RuSr2Eu1.2Ce0.8Cu2O10 system. In this case, however, the magnetic order that has been observed is associated with an impurity phase; no magnetic order associated with the titled compound has been found so far ().
See the related topics
Spin Dynamics in Electron-doped Cuprate Superconductors
Some
Examples of Magnetic Superconductor Publications:
Direct Observation of Long Range Ferromagnetic Order in the Reentrant Superconductor HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, D. E. Moncton, W. Thomlinson, G. Shirane and R. N. Shelton, Sol. St. Comm. 26, 493 (1978).
Neutron Diffraction Study of Magnetic Order in the Ternary Superconductor ErMo6Se8, J. W. Lynn, D. E. Moncton, G. Shirane, W. Thomlinson, J. Eckert and R. N. Shelton, J. Appl. Phys. 49, 1389 (1978).
Magnetic Properties of the Superconducting Alloy System (Ce1-cHoc)Ru2: A Neutron Scattering Study, J. W. Lynn and C. J. Glinka, J. Mag. and Mag. Materials 14, 179 (1979).
Magnetic Correlations and Crystal-Field Levels in the Superconductor (Ce.73Ho.27)Ru2, J. W. Lynn, D. E. Moncton, L. Passell, and W. Thomlinson, Phys. Rev. B 21, 70 (1980).
Neutron Scattering Studies of Magnetic Superconductors, J. W. Lynn and R. N. Shelton, J. Mag. and Mag. Materials 18, 1577 (1980).
Competition Between Ferromagnetism and Superconductivity in HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, G. Shirane, W. Thomlinson and R. N. Shelton, Phys. Rev. Lett. 46, 368 (1981).
Observation of Long Range Oscillatory Magnetic Order in the Reentrant Superconductor HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, J. L. Ragazzoni, R. Pynn and J. Joffrin, J. de Physique Lettres 42, L45 (1981).
Neutron Scattering Studies of the Magnetic Superconductor (Ce1-xTbx)Ru2, J. A. Fernandez-Baca and J. W. Lynn, J. Appl. Phys. 52, 2183 (1981).
Magnetic Properties of the Reentrant Ferromagnetic Superconductor HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, G. Shirane, W. Thomlinson, R. N. Shelton and D. E. Moncton, Phys. Rev. B 24, 3817 (1981).
Formation of an Oscillatory Magnetization Near the Reentrant Superconducting Transition in HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, R. Pynn, J. Joffrin, and J. L. Ragazzoni, Physica 108B, 801 (1981).
Evolution from Ferromagnetism to Spin Glass Behavior in Amorphous (Fe1-xNix).75P.16B.06Al.03, J. W. Lynn, R. W. Erwin, H. S. Chen and J. J. Rhyne, Solid State Commun. 46, 317 (1983).
Field Dependence of the Oscillatory Magnetic State in Superconducting HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, R. Pynn, J. L. Raggazoni, and J. Joffrin, J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 32, 493 (1983).
Investigation of the Magnetic and Superconducting Properties of (Er1-xHox)Rh4B4, J. W. Lynn, R. N. Shelton, H. E. Horng and C. J. Glinka, Physica 120B, 224 (1983).
Investigation of the Modulated Magnetic Phase of HoMo6S8, J. W. Lynn, R. Pynn, J. Joffrin, J. L. Ragazzoni and R. N. Shelton, Phys. Rev. B27, 581(RC) (1983).
Neutron Scattering Studies of Phase Transitions in Superconductors, J. W. Lynn, J. Less Comm. Metals 94, 75 (1983).
Magnetic Ordering in Superconductors, R. Pynn, J. W. Lynn and J. Joffrin, Helvetica Physica Acta 56, 179 (1983).
Temperature-Dependent Sinusoidal Magnetic Order in the Superconductor HoMo6Se8, J. W. Lynn, J. A. Gotaas, R. W. Erwin, R. A. Ferrell, J. K. Bhattacharjee, R. N. Shelton and P. Klavins, Phys. Rev. Lett. 52, 133 (1984).
Magnetic and Superconducting Properties of Holmium-Rich (Er1-xHox)Rh4B4, J. W. Lynn, J. A. Gotaas, R. N. Shelton, H. E. Horng and C. J. Glinka, Phys. Rev. B31, 5756 (1985).
Magnetic Field Dependence of the Small-Angle Neutron Scattering in HoMo6Se8, J. A. Gotaas and J. W. Lynn, J. Mag. Mag. Matr. 54-57, 1529 (1986).
Magnetic Fluctuations and Two-Dimensional Ordering in ErBa2Cu3O7, J. W. Lynn, W.-H. Li, Q. Li, H. C. Ku, H. D. Yang and R. N. Shelton, Phys. Rev. B 36, 2374(RC) (1987).
Suppression of Superconductivity by Antiferromagnetism in Tm2Fe3Si5, J. A. Gotaas, J. W. Lynn, R. N. Shelton, P. Klavins, and H. F. Braun, Phys. Rev. B36, 7277 (RC) (1987).
Absolute Measurement of the Ordered Magnetic Moment in Holmium Rich (Er1-xHox)Rh4B4, Q. Li, J. W. Lynn and J. A. Gotaas, Phys. Rev. B35, 5008 (1987).
Antiferromagnetic Structure of the Cubic Superconductor ErPd2Sn, H. B. Stanley, J. W. Lynn, R. N. Shelton and P. Klavins, J. Appl. Phys. 61, 3371 (1987).
Effects of Crystal Anisotropy on Magnetization and Magnetic Order in Superconducting RBa2Cu3O7-x, R. N. Shelton, R. W. McCallum, M. A. Damento, K. A. Gschneidner, Jr., H. C. Ku, H. D. Yang, J. W. Lynn, W-H. Li, and Q. Li, Physica 148B, 285 (1987).
Two-Dimensional Character of the Magnetic Order in ErBa2Cu3O7, J. W. Lynn, W-H. Li, Q. Li, H. C. Ku, H. D. Yang and R. N. Shelton, Rev. Sol. St. Phys. 1, 357 (1987).
Nature of the Magnetic Order of Cu in Oxygen Deficient RBa2Cu3O6+x, J. W. Lynn, W-H. Li, H. A. Mook, B. C. Sales, and Z. Fisk, Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2781 (1988).
Antiferromagnetic Order of the Cu in RBa2Cu3O6+x, J. W. Lynn, W-H. Li, H. A. Mook, B. C. Sales and Z. Fisk, J. de Physique 49, C8-1, 2153 (1988).
Antiferromagnetic Structure and Crystal Field Splittings in the Cubic Heusler Alloys HoPd2Sn and ErPd2Sn, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, H. B. Stanley, T. J. Udovic, R. N. Shelton and P. Klavins, J. de Physique 49, C8-1, 373 (1988).
Long Range Antiferromagnetic Order of the Cu in Oxygen-Deficient, RBa2Cu3O6+x, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, H. A. Mook, B. C. Sales and Z. Fisk, Phys. Rev. B37, 9844 (RC) (1988).
Magnetic Order in RBa2Cu3O6+x, J. W. Lynn and W-H. Li, J. Appl. Phys. 64, 6065 (1988).
Magnetic Order of Pr in PrBa2Cu3O7, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, S. Skanthakumar, T. W. Clinton, A. Kebede, C.-S. Jee, J. E. Crow, and T. Mihalisin, Phys. Rev. B 40, 5300 (1989).
Pressure Dependence of the Cu Magnetic Order in NdBa2Cu3O6+x, J. W. Lynn, W-H. Li, S. F. Trevino and Z. Fisk, Phys. Rev. B40, 5172 (1989).
Magnetic Phase Transitions and Structural Distortion in Nd2CuO4, S. Skanthakumar, H. Zhang, T. W. Clinton, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, Z. Fisk, and S-W. Cheong, Physica C 160, 124 (1989).
2-D and 3-D Magnetic Behavior of Er in ErBa2Cu3O7, J. W. Lynn, T. W. Clinton, W-H. Li, R. W. Erwin, J. Z. Liu, K. Vandervoort, R. N. Shelton and P. Klavins, Phys. Rev. Lett. 63, 2606 (1989).
Antiferromagnetic Ordering in Superconducting and Oxygen-Deficient non-Superconducting RBa2Cu3O7-d Compounds (R = Nd and Sm), K. N. Yang, J. M. Ferreira, B. W. Lee, M. B. Maple, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, and R. W. Erwin, Phys Rev. B40, 10963 (1989).
Magnetic Ordering of Nd in (Nd-Ce)2CuO4, J. W. Lynn, S. Skanthakumar, I. W. Sumarlin, W-H. Li, R. N. Shelton, J. L. Peng, Z. Fisk, and S-W. Cheong, Phys. Rev. B 41, 2569 (1990).
Magnetic Order of the Cu Planes and Chains in NdBa2Cu3O6+x, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, and Z. Fisk, Phys. Rev. B41, 4098 (1990).
Two-Dimensional Magnetic Order of Er in ErBa2Cu3O7, J. W. Lynn, T. W. Clinton, W-H. Li, R. W. Erwin, J. Z. Liu, R. N. Shelton, and P. Klavins, J. Appl. Phys. 67, 4533 (1990).
Magnetic Order and Spin Fluctuations in Oxide Superconductors, J. W. Lynn, Physica B 163, 69 (1990).
Magnetic Phase Transitions in Nd2CuO4, S. Skanthakumar, H. Zhang, T. W. Clinton, I. W. Sumarlin, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, Z. Fisk, and S-W. Cheong, J. Appl. Phys. 67, 4530 (1990).
Magnetic Properties of Pr in PrBa2Cu3O7, S. Skanthakumar, W-H. Li, J. W. Lynn, A. Kebede, J. E. Crow, and T. Mihalisin, Physica B 163, 239 (1990).
Two- and Three-Dimensional Magnetic Order of the Rare Earth Ions in RBa2Cu4O8, H. Zhang, J. W. Lynn, W-H. Li, T. W. Clinton, and D. E. Morris, Phys. Rev. B41, 11229 (1990).
On the Crystal and Spin Structure of Nd2CuO4, S. Skanthakumar and J. W. Lynn, Physica C170, 175 (1990).
Magnetic Ordering of the Cu Spins in PrBa2Cu3O6+x, N. Rosov, J. W. Lynn, G. Cao, J. W. O'Reilly, P. Pernambuco-Wise and J. E. Crow, Physica C 204, 171 (1992).
Magnetic Ordering of Sm in Sm2CuO4, I. W. Sumarlin, S. Skanthakumar, J. W. Lynn, J. L. Peng, W. Jiang, Z. Y. Li and R. L. Greene, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2228 (1992).
Observation of Oscillatory Magnetic Order in the Reentrant Antiferromagnetic Superconductor HoNi2B2C, T. E. Grigereit, J. W. Lynn, Q. Huang, A. Santoro, R. J. Cava, J. J. Krajewski, and W. F. Peck, Jr., Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 2756 (1994).
Magnetic Ordering and Crystallographic Structures in the Superconducting RNi2B2C Materials, J. W. Lynn, S. Skanthakumar, Q. Huang, S. K. Sinha, Z. Hossain, L. C. Gupta, R. Nagarajan, and C. Godart, Phys. Rev. B 55, 6584 (1997).
Antiferromagnetic Order of the Ru and Gd in Superconducting RuSr2GdCu2O8, J. W. Lynn, B. Keimer, C. Ulrich, C. Bernhard, and J. L. Tallon, Phys. Rev. B 61, R14964 (2000).
Pr Magnetic Order and Spin Dynamics in Cuprates, J. W. Lynn, N. Rosov, S. N. Barilo, L. Kurnevitch, and A. Zhokhov, Chinese Journal of Physics 38, 286 (2000).
Direct Observation of Spontaneous Weak-Ferromagnetism in the Superconductor ErNi2B2C, S. -M. Choi, J. W. Lynn, D. Lopez, P. L. Gammel, P. C. Canfield and S. L. Bud'ko, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 107001 (2001).
Magnetic Order in YBa2Cu3O6+x Superconductors, H. A. Mook, P. Dai, S. M. Hayden, A. Hiess, J. W. Lynn, S-H. Lee, and F. Dogan, Phys. Rev. B 66, 144513 (2002).
Antiferromagnetic Order as the Competing Ground State in Electron Doped Nd1.85Ce0.15CuO4, H. J. Kang, P. Dai, J. W. Lynn, M. Matsuura, J. R. Thompson, S-C. Zhang, D. N. Argyriou, Y. Onose, and Y. Tokura, Nature 423, 522 (2003).
Reply to Comment on "Antiferromagnetic Order as the Competing Ground State in Electron-doped Nd1.85Ce0.15CuO4", H. J. Kang, P. Dai, J. W. Lynn, M. Matsuura, J. E. Thompson, S-C Zhang, D. N. Argyriou, Y. Onose, and Y. Tokura, Nature 426, 140 (2003).
Effect of a Magnetic Field on the Long-range Magnetic Order in insulating Nd2CuO4 and superconducting Nd1.85Ce0.15CuO4, M. Matsuura, P. Dai, H. J. Kang, J. W. Lynn, D. N. Argyriou, K. Prokes, Y. Onose, and Y. Tokura, Phys Rev. B 68, 144503 (2003).
"Spin-Flop" Transition and Anisotropic Magnetoresistance in Pr1.3-xLa0.7CexCuO4: Unexpectedly Strong Spin-Charge Coupling in Electron-Doped Cuprates, A. N. Lavrov, H. J. Kang, Y. Kurita, T. Suzuki, S. Koniya, J. W. Lynn, S-H. Lee, P. Dai, and Y. Ando, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 227003 (2004).
Magnetic Field Effect on Static Antiferromagnetic Order Above the Upper Critical Field in Nd1.85Ce0.15CuO4, M. Matsuura, P. Dai, H. J. Kang, J. W. Lynn, D. N. Argyriou, Y. Onose, and Y. Tokura, Phys Rev. B 69, 104510 (2004).
Electronic Inhomogeneity and Competing Phases in Electron-doped superconducting Pr0.88LaCe0.12CuO4-x, H. J. Kang, P. Dai, H. A. Mook, M. Matsuura, J. W. Lynn, Y. Kurity, S. Komiya, and Y. Ando, Phys. Rev. B 71, 100502 (Rapid Communications) (2005).
Electronically Competing Phases and Their Magnetic Field Dependence in Electron-doped Nonsuperconducting and Superconducting Pr1.88LaCe0.12CuO4+-d, H. J. Kang, P. Dai, H. A. Mook, D. N. Argyriou, V. Sikolenko, J. W. Lynn, Y. Kurita, S. Komiya, and Y. Ando, Phys. Rev. B 71, 214512 (2005).
Neutron Scattering Study of La1.9Ca1.1Cu2O6+d and La1.85Sr0.15CaCu2O6+d, M. Hucker, Y.-J. Kim, G. D. Gu, J. M. Tranquada, B. D. Gaulin, and J. W. Lynn, Phys. Rev. B 71, 094510 (2005).
Search for Magnetic Order in Superconducting RuSr2Eu1.2Ce0.8Cu2O10, J. W. Lynn, Y. Chen, Q. Huang, S. K. Goh, and G. V. M. Williams, Phys. Rev. B 76, 014519 (2007).
Magnetic Order Close to Superconductivity in the Iron-based Layered La(O1-xFx)FeAs systems, C. de la Cruz, Q. Huang, J. W. Lynn, J. Li, W. Ratcliff II, J. L. Zarestky, H. A. Mook, G. F. Chen, J. L. Luo, N. L. Wang, and P. Dai, P. Dai, Nature 453, 899 (2008). Supplementary Material.
Magnetic Order of the Iron Spins in NdOFeAs, Y. Chen, J. W. Lynn, G. F. Chen, G. Li, Z. C. Li, J. L. Luo, N. L. Wang, P. Dai, C. dela Cruz, and H. A. Mook Phys. Rev. B 78, 064515 (2008).
Intrinsic Properties of Stoichiometric LaOFeP, T. M. McQueen, M. Regulacio, A. J. Williams, Q. Huang, J. W. Lynn, Y. S. Hor, D.V. West, and R. J. Cava, Phys. Rev. B 78, 024521 (2008).
Doping Evolution of Antiferromagnetic Order and Structural Distortion in LaFeAsO1-xFx, Q. Huang, J. Zhao, J. W. Lynn, G. F. Chen, J. L. Lou, N. L. Wang, and P. Dai, Phys. Rev. B 78, 054529 (2008).
Structural and Magnetic Phase Diagram of CeFeAsO1-xFx and its Relationship to High-Temperature Superconductivity, J. Zhao, Q. Huang, C. de al Cruz, S. Li, J. W. Lynn, Y. Chen, M. A. Green, G. F. Chen, G. Li, Z. C. Li, J. L. Luo, N. L. Wang, and P. Dai, Nature Materials 7, 953 (2008).
Spin and Lattice Structure of Single Crystal SrFe2As2, Jun Zhao, W. Ratcliff-II, J. W. Lynn, G. F. Chen, J. L. Luo, N. L. Wang, Jiangping Hu, and Pengcheng Dai, Phys. Rev. B 78, 140504(R) (2008).
Low energy spin waves and magnetic interactions in SrFe2As2, J. Zhao, D.-X. Yao, S. Li, T. Hong, Y. Chen, S. Chang, W. Ratcliff II, J. W. Lynn, H. A. Mook, G. F. Chen, J. L. Luo, N. L. Wang, E. W. Carlson, J. Hu, and P. Dai, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 167203 (2008).
Lattice and Magnetic structures of PrFeAsO, PrFeAsO0.85F0.15 and PrFeAsO0.85, Jun Zhao, Q. Huang, Clarina de la Cruz, J. W. Lynn, M. D. Lumsden, Z. A. Ren, Jie Yang, Xiaolin Shen, Xiaoli Dong, Zhongxian Zhao, and Pengcheng Dai, Phys. Rev. B 78, 132504 (2008).
Pressure-induced Volume-collapsed Tetragonal Phase of CaFe2As2 as seen via Neutron Scattering, A. Kreyssig, M. A. Green, Y. B. Lee, G. D. Samolyuk, P. Zajdel, J. W. Lynn, S. L. Bud'ko, M. S. Torikachvili, N. Ni, S. Nandi, J. Leao, S. J. Poulton, D. N. Argyriou, B. N. Harmon, P. C. Canfield, R. J. McQueeney, and A. I. Goldman, Phys. Rev. B 78, 184517 (2008).
The crystalline electric field as a probe for long range antiferromagnetic order and superconductivity in CeFeAsO1−xFx, S. Chi, D. T. Adroja, T. Guidi, R. Bewley, Shliang Li, Jun Zhao, J. W. Lynn, C. M. Brown, Y. Qiu, G. F. Chen, J. L. Lou, N. L. Wang, and Pengcheng Dai, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 217002 (2008).
Neutron Studies of the Iron-based Family of High Tc Magnetic Superconductors, J. W. Lynn, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1148E (2008).
Magnetic order in BaFe2As2, the parent compound of the FeAs based superconductors in a new structural family, Q. Huang, Y. Qiu, W. Bao, J.W. Lynn, M.A. Green, Y.C. Gasparovic, T. Wu, G. Wu, and X. H. Chen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 257003 (2008).
Crystal Structure and Antiferromagnetic Order in NdFeAsO1-xFx (x=0.0 and 0.2)
Superconducting Compounds from Neutron Diffraction Measurements, Y. Qiu, W. Bao, Q. Huang, T. Yildirim, J. M.
Simmons, M. A. Green, J.W. Lynn, Y.C. Gasparovic, J. Li, T. Wu, G. Wu, and
X.H. Chen,
Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 257002 (2008).
Neutron
Studies of the Iron-based Family of High TC Magnetic Superconductors,
Jeffrey W. Lynn and Pengcheng Dai,
Physica C
469. 469 (2009).
Lattice Collapse and Quenching of Magnetism in CaFe2As2 under Pressure: A
Single Crystal Neutron and X-ray Diffraction Investigation, A. I.
Goldman, A. Kreyssig, K. Prokes, D. K. Pratt, D. N. Argyriou, J. W. Lynn, S.
Nandt, S. A. Kimber, Y. Chen, Y. B. Lee, G. Samolyuk, J. Leao, S. J. Poulton,
S. L. Bud'ko, N. Ni, P. C. Canfield, B. N. Harmon, and R. J. McQueeney, Phys. Rev. B 79,
024513 (2009).
First-order Magnetic and Structural Phase Transitions in Fe1+ySexTe1-x,
S. Li, C. de la Cruz, Q. Huang, Y. Chen, J. W. Lynn, J. Hu, Y-L Huang, F-C.
Hsu, K-W. Yeh, M-K. Wu, and P. Dai,
Phys. Rev. B 79,
054503 (2009).
Spin Gap and Magnetic Resonance in Superconducting BaFe1.9Ni0.1As,
S. Li, Y. Chen, S. Chang, J. W. Lynn, L. Li, Y. Luo, G. Cao, Z. Xu, and P.
Dai,
Phys. Rev. B
79, 174527 (2009).
Commensurate Magnetic Structure in CeRhIn4.85Hg0.15,
W. Bao, Y. C. Gasparovic, J. W. Lynn, F. Ronning, E. D. Bauer, J. D.
Thompson, and Z. Fisk,
Phys. Rev. B
79, 092415 (2009).
Magnetic Ordering in Electronically Phase Separated Sr/O co-doped La2-xSrxCuO4+y,
L. Udby, N. H. Andersen, K. Lefmann, B. O. Wells, H. E. Mohottala, C.
Niedermayer, N. B. Christensen, J. W. Lynn, and F. C. Chou,
Phys. Rev. B
80, 014505 (2009).
Magnetic Structures of the Quaternary Intermetallic Borocarbides RCo2B2C
(R=Dy, Ho, Er), M. El Massalami, R. Moreno, H. Takeya, B. Ouladdiaf, J.
W. Lynn, and R. S. Freitas,
J. Phys.: Cond. Matt.
21,
436006 (2009).
Lattice distortion and Magnetic Quantum Phase Transition in CeFeAs1-xPxO,
C. de la Cruz, W. Z. Hu, S. Li, Q. Huang, J. W. Lynn, M. A. Green, G. F.
Chen, N. L. Wang, H. A. Mook, Q. Si, and P. Dai, (submitted).
Evolution of the bulk properties, structure, magnetic order, and
superconductivity with Ni doping in CaFe2-xNixAs2,
Neeraj Kumar, Songxue Chi, Ying Chen, Gaurav Rana, A. K. Nigam, A.
Thamizhavel, W. Ratcliff II, S. K. Dhar, and Jeffrey W. Lynn,
Phys. Rev. B
80, 144524 (2009).
Lattice distortion and Magnetic Quantum Phase Transition in CeFeAs1-xPxO,
C. de la Cruz, W. Z. Hu, S. Li, Q. Huang, J. W. Lynn, M. A. Green, G. F.
Chen, N. L. Wang, H. A. Mook, Q. Si, and P. Dai,
Phys. Rev. Lett.
104, 017204 (2010).
Magnetic Form Factor of SrFe2As2: Neutron
Diffraction Measurements, W. Ratcliff
II, P. A. Kienzle, J. W. Lynn, S. Li, P. Dai, G. F. Chen and N. L. Wang,
Phys. Rev. B
81, 140502(R) (2010).
Electron-doping Evolution of the Low-energy Spin Excitations in the Iron
Arsenide BaFe2-xNixAs2 Superconductors,
Miaoyin Wang, Huiqian Luo, Jun Zhao, Chenglin Zhang, Meng Wang, Karol J.
Marty, Songxue Chi, Jeffrey W. Lynn, Astrid Schneidewind, Shiliang Li, and
Pengcheng Dai,
Phys. Rev.
B
81, 174524 (2010).
Cd-doping effects in Ce2MIn8 (M=Rh and Ir) Heavy
Fermion Compounds, C. Adriano, C. Giles, E. M. Bitter, L. N. Coelho, F.
de Bergevin, C. Mazzoll, L. Paolasini, W. Ratcliff, R. Bindel, J. W. Lynn,
Z. Gisk, and P. G. Pagliuso,
Phys. Rev. B
81, 245115 (2010).
Doping Dependence of Spin Dynamics in Electron-Doped Ba(Fe1−xCox)2As2,
K. Matan, S. Ibuka, R. Morinaga, S. X. Chi, J. W. Lynn, A. D. Christianson,
M. D. Lumsden, and T. J. Sato,
Phys. Rev. B
82, 054515 (2010).
Interplay between Fe and Nd magnetism in NdFeAsO single crystals, W.
Tian, W. Ratcliff II, J. W. Lynn, J.-Q. Yan, M.G. Kim, B. Jensen, K. Dennis,
R.W. McCallum, T.A. Lograsso, R.J. McQueeney, A.I. Goldman, A. Kreyssig,
Phys. Rev. B
82, 060514(R) (2010).
Antiferromagnetic Critical Fluctuations in BaFe2As2,
Stephen D. Wilson, Z. Yamani, C. R. Rotundu, B. Freelon, P. N. Valdivia, E.
Bourret-Courchesne, J. W. Lynn, Songxue Chi, Tao Hong, and R. J. Birgeneau,
Phys. Rev. B
82, 144502 (2010).
Magnetic Field Effect on the Static Antiferromagnetic Order and Spin
Excitations in the Underdoped Iron Arsenide Superconductor BaFe1.92Ni0.08As2,
M Wang, H. Luo, M. Wang, S. Chi, J. A. Rodriguez-Rivera, D. Singh, S. Chang,
J. W. Lynn, and P. Dai,
Phys. Rev.
B
83, 094516 (2011).
Superconductivity at 45 K in the Collapsed Tetragonal Phase of
Electron-doped CaFe2As2, S. R. Saha, N. P. Butch,
T. Drye, J. Magill, S. Ziemak, K. Kirshenbaum, P. Y. Zavalij, J. W. Lynn,
and J. Paglione, (submitted).